HackerRank - Prepare|Algorithms|Strings|Separate the Numbers
A numeric string, , is beautiful if it can be split into a sequence of two or more positive integers, , satisfying the following conditions:
- for any (i.e., each element in the sequence is more than the previous element).
- No contains a leading zero. For example, we can split into the sequence , but it is not beautiful because and have leading zeroes.
- The contents of the sequence cannot be rearranged. For example, we can split into the sequence , but it is not beautiful because it breaks our first constraint (i.e., ).
The diagram below depicts some beautiful strings:
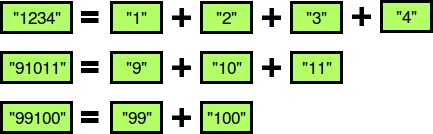
Perform queries where each query consists of some integer string . For each query, print whether or not the string is beautiful on a new line. If it is beautiful, print YES x, where is the first number of the increasing sequence. If there are multiple such values of , choose the smallest. Otherwise, print NO.
Function Description
Complete the separateNumbers function in the editor below.
separateNumbers has the following parameter:
- s: an integer value represented as a string
Prints
- string: Print a string as described above. Return nothing.
Input Format
The first line contains an integer , the number of strings to evaluate.
Each of the next lines contains an integer string to query.
Constraints
Sample Input 0
7
1234
91011
99100
101103
010203
13
1
Sample Output 0
YES 1
YES 9
YES 99
NO
NO
NO
NO
Explanation 0
The first three numbers are beautiful (see the diagram above). The remaining numbers are not beautiful:
- For , all possible splits violate the first and/or second conditions.
- For , it starts with a zero so all possible splits violate the second condition.
- For , the only possible split is , which violates the first condition.
- For , there are no possible splits because only has one digit.
Sample Input 1
4
99910001001
7891011
9899100
999100010001
Sample Output 1
YES 999
YES 7
YES 98
NOimport java.io.*;import java.math.*;import java.security.*;import java.text.*;import java.util.*;import java.util.concurrent.*;import java.util.function.*;import java.util.regex.*;import java.util.stream.*;import static java.util.stream.Collectors.joining;import static java.util.stream.Collectors.toList;
class Result {
/* * Complete the 'separateNumbers' function below. * * The function accepts STRING s as parameter. */
public static void separateNumbers(String s) { int numSize = 1; while (numSize<s.length()/2+1 && !s.startsWith("0")) { String strInitialNum = s.substring(0, numSize); long initialNum = Long.parseLong(strInitialNum); String genStr = ""; while (genStr.length() < s.length()) { genStr+= initialNum; initialNum++; }
if(genStr.equals(s)){ System.out.println("YES "+strInitialNum); return; } numSize++;
System.out.println(genStr); } System.out.println("NO");
}
}
class Solution { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int q = Integer.parseInt(bufferedReader.readLine().trim());
IntStream.range(0, q).forEach(qItr -> { try { String s = bufferedReader.readLine();
Result.separateNumbers(s); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new RuntimeException(ex); } });
bufferedReader.close(); }}
Comments
Post a Comment